GeoGebra is a great tool for visualizing spheres in 3D, and for finding the sphere’s radius and center.
GeoGebra Instruction 1
Drawing a Sphere
- 1.
- Open
Algebra Viewand3D GraphicsunderViewinMenu. - 2.
- If you know the equation of the sphere, you can type it in
Algebra Viewas it is. The sphere will now appear inAlgebra Viewas an equation. The sphere will also be drawn in3D Graphics.If you know the sphere’s radius and center, use the command
Sphere(<point>, <radius>)
where
<point>is the center and<radius>is the radius of the sphere. The sphere will now appear inAlgebra Viewas an equation. The sphere will also be drawn in3D Graphics.
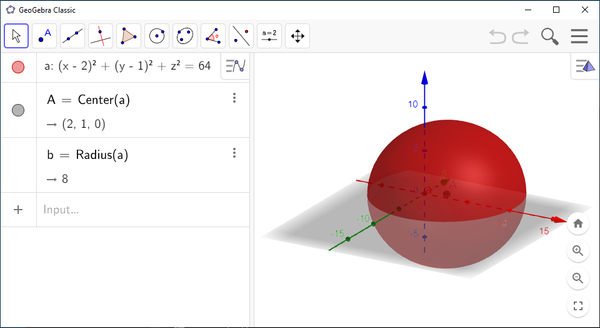
Example 1
I want to draw the sphere given by the equation
which is a sphere with center and radius 8. Following the instructions above, I get the sphere pictured below.
GeoGebra Instruction 2
Finding the Radius and Center of a Sphere
- 1.
- Open
Algebra Viewand3D GraphicsunderViewinMenu. - 2.
- Enter the equation of the sphere, as given in your exercise. The sphere is now shown in
Algebra Viewas an equation. It’s also displayed as a surface in3D Graphics. - 3.
- You get the radius of the sphere by using the command
Radius(<conic>)
where
<conic>is the name of the equation in Item 2. - 4.
- You get the center by using the command
Center(<conic>)
where
<conic>is the name of the equation in Item 2.






